Full code checking can be performed on Dimension Lumber and Post and Timber size wood shapes based on the following codes:
Note
Glu-Lams are treated as any other wood species and may be selected from the list of species on the Wood tab of the Materials spreadsheet.
Available Glulam Materials are per Tables 5A and 5C of the NDS Supplement and Table 6.3 of the CSA O86. When a Glu-Lam is selected, the grade will be listed as "na" or not applicable.
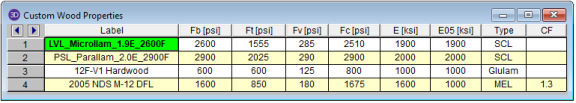
If you prefer to use a material that is not listed in the design code glulam tables, please enter the material type as a Custom Wood Species.
Note
All Glu-Lam members should be dimensioned as "Full Sawn" using the format wXdFS (or wXdMFS for metric sizes), where "w" and "d" are the actual width and depth dimensions. If the size is entered as wXd without the FS designation, then the size will be assumed to be regular dimensional lumber.
RISA includes two redesign lists for Glu-Lams: Glu-Lam_Western for Western Species and Hardwoods (HW), and Glu-Lam_SouthernPine for Southern Pine (SP/SP).
Please note that glulam design is not supported for the 91/97 NDS design code.
To use a custom
wood material that is not part of the standard NDS or CSA O86 databases, you will
need to define the custom design properties.
To access the Custom Wood Properties spreadsheet, select Custom Wood Species from the Spreadsheets menu.

Notes:
Create and apply your custom material by doing the following:
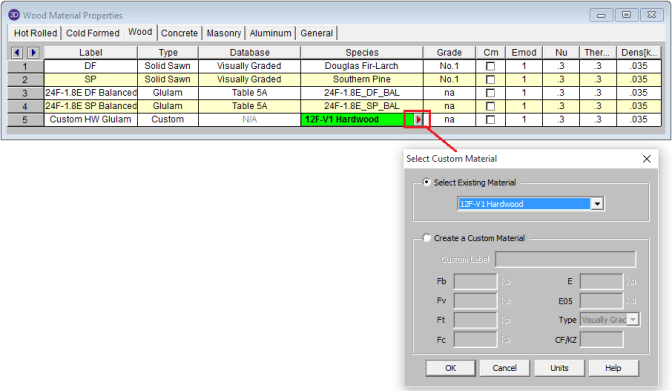
Note
For additional advice on this topic, please see the RISA Tips & Tricks webpage at risa.com/post/support. Type in Search keywords: Custom Wood Species.
The Member Design Parameters spreadsheet records the design parameters
for the timber code checks and may be accessed by selecting
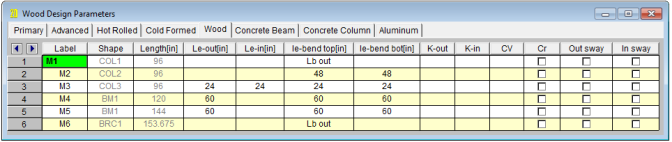
These parameters are defined for each member.
You may assign a unique Label to all of the members. Each label
must be unique, so if you try to enter the same label more than once you
will get an error message.
The member Shape or Section Set is reported in the second column. This value is listed for reference only and may not be edited as it is dictated by the entry in the Section/Shape column on the Primary tab.
The
See the Unbraced Lengths topic.
See the Unbraced Lengths topic.
Please see below for information about the various wood adjustment factors.
See the Unbraced Lengths topic.
The NDS design codes have a number of adjustment factors that are applied to the various allowable stresses to determine the capacity of the member. The adjustment factors are summarized in section 2.3 of the code. The following topics help to summarize how adjustment factors are obtained and used.
Note
CD is the Load Duration adjustment factor used for ASD codes. It is entered on the Load Combinations spreadsheet for each load combination for which you want wood code check results. The CD factor must be entered for each individual load combination because the CD factor is dependent on the types of loads that are applied in each load combination. Therefore, different load combinations could have different CD factors. For example, per the NDS 2018 specification, a load combination that had only dead load, would have a CD factor of “0.9”, while another combination that was comprised of dead load plus wind load would have a CD factor of “1.6”.
The CD factor will only be applied to wood code checks on wood members. See Table 2.3.2 in the NDS 2018 specification for the CD factors to be applied for typical loads. Appendix B has additional information about the Load Duration Factor.
Note
Cm is the Wet Service adjustment factor. It is applied when you check the Cm checkbox in the Materials Spreadsheet.
Ci is the Incision factor per Table 4.3.8 of NDS code. It is applied when you check the Ci checkbox in the Materials Spreadsheet.
Ct is the Temperature adjustment factor. It is calculated internally based on the wood Temperature value set on the Codes tab of Model Settings. See section 2.3.3 of the NDS 2018 for more information on this factor.
The Column Stability Factor, CP, and the Beam Stability Factor, CL,
are calculated internally. These calculated values are shown on
the Wood tab of the
The value of Emin used for the calculation of these factors is calculated using equation D-4 from appendix D of the 2018 NDS. For some members (especially for glulams) this equation may produce a slightly more accurate value of Emin that shown in the NDS tables.
Note
CF is the Size adjustment factor. It is applied automatically when you assign a wood shape from the NDS shape database. See Tables 4A, 4B, 4D, and 4E in the NDS supplement for information on the CF factor.
Note:
CV is the Volume adjustment factor. It is applied automatically when you assign a glulam or SCL material member. The user can override the calculated value by manually entering the factor on the Wood tab of the Members Spreadsheet.
Note:
Cfu is the Flat Use adjustment factor. is automatically applied to the weak axis allowable bending stress of a wood member whenever weak axis moments are present. See the tables in the NDS supplement for more information on this factor.
Note
Cr is the Repetitive Member adjustment factor. This factor specifies if the beam is one of a group of repetitive members. This design parameter can be set on the Wood tab of the Members Spreadsheet. If you put a check in the Cr field, a factor of 1.15 will be applied to beam members that are 2" to 4" thick. See the section 4.3.9 of the NDS 2018 for information on this factor.
Note
CH is the Shear Stress adjustment factor. This design parameter can be set on the Wood tab of the Members Spreadsheet. If left blank the program will use a default value of 1.0. See the tables in the NDS supplement for information on other CH factors.
Note
Cf is the Form adjustment factor. It is applied automatically when designing by the NDS 91/97 or 2001 Specification and a 'Round' shape is selected from the NDS shape database. See section 2.3.8 in the NDS (91/97, 2001) for information on the Cf factor.
Note
Kf is the format conversion factor for LRFD design only. The tabulated reference design values provided in the NDS Supplement contain safety adjustments appropriate for ASD. The Kf factor converts these values to nominal design values for LRFD. These factors are provided in NDS Table 4.3.1 and Appendix N.
Phi is the resistance factor for LRFD design only. These values are provided in NDS Table 4.3.1 and are dependent on the property ranging from 0.75 for shear and 0.90 for compression.
Lambda is the Time Effect adjustment factor used for LRFD codes. It is entered on the Load Combinations spreadsheet for each load combination for which you want wood code check results. The lambda factor must be entered for each individual load combination because the lambda factor is dependent on the combination of loads. Therefore, different load combinations could have different lambda factors. For example, per the NDS 2018 specification, a load combination that had only dead load, would have a CD factor of “0.6”, while another combination that was comprised of dead load plus wind load would have a CD factor of “1.0”.
The lambda factor will only be applied to wood code checks on wood members. See Table N3 in the NDS 2018 specification for the lambda factors to be applied for typical load combinations.
The CSA O86 design code has a number of adjustment factors that are applied to the various allowable stresses to determine the capacity of the member. The adjustment factors are summarized in clause 4.3 of the code. The following topics help to summarize how adjustment factors are obtained and used.
Note
KD is the Load Duration adjustment factor. It is entered on the Load Combinations spreadsheet for each load combination for which you want wood code check results. The KD factor must be entered for each individual load combination because the factor is dependent on the types of loads that are applied in each load combination. Therefore, different load combinations could have different KD factors. For example, per the CSA O86 -2009 specification, a load combination that had only dead load, would have a KD factor of 0.65, while another combination that was comprised of dead load plus wind load would have a KD factor of 1.15.
The KD factor will only be applied to wood code checks on wood members. See Table 5.3.2.2 in the CSA O86 - 2014 specification for the KD factors to be applied for typical loads.
Note
Ks is the Service Condition adjustment factor. It is applied when you check the Ks check-box in the Materials Spreadsheet. See clause 6.4.2 (sawn lumber) or clause 7.4.2 (glulams) in the CSA O86-14 for more information on this factor.
CV is the Shear Load coefficient for glulam members. It is applied automatically when you assign a material from the CSA Table 7.3 glulam material database. By default this value will always be taken as 1.0. However, the user can override this value by manually entering the factor on the Wood tab of the Members Spreadsheet.
KH is the System adjustment factor. This factor depends on the System Factor selection applied to the member on the Wood tab of the Members spreadsheet:
Note
KZ is the Size factor. It is applied automatically when you assign a wood shape from the CSA shape database. See Table 6.4.5 in the CSA O86-14 design code for information on this factor.
KL is the Lateral Stability factor. This factor is calculated internally per the equation given in clause 7.5.6.4.4 for both glulam and full sawn members.
The final calculated values of both CB and KL are shown on
the Wood tab of the
Note:
KC is the Slenderness factor. This factor is calculated internally per the equation given in clause 6.5.6.2.4 for full sawn members and per clause 7.5.8.5 for glulam members.
Note:
The Flat Use factor is just called "Flat Use" in the member detail report. There is no explicit factor for this defined in the CSA O86-14 design code. However, there is a note for Table 6.3.1C (Material Strengths for Beams and Stringers) that includes a flat use adjustment factor. The program will determine this factor based on the asterisk table under Table 6.3.1C.
RISA will calculate the Emin value for NDS wood materials rather than read it in from the design tables. In the 2018 edition of the NDS, Emin is calculated per equation (D-4) from Appendix D.
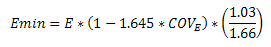
COVE (the coefficient of variation in modulus of elasticity) comes from Table F1 in Appendix F.
Note
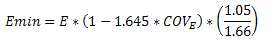
Access the Wood Code Checks Spreadsheet
by selecting the Results menu and then selecting Members![]() Design Results and then clicking the Wood tab.
Design Results and then clicking the Wood tab.
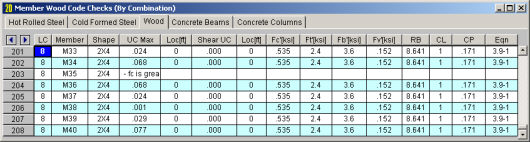
The final result of the design solution are the code check values (ratios of actual stress to allowable stress). So, if these values are less than 1.0, the member passes. If they are greater than 1.0, the member fails.
Note:
The UC Max value represents the combined bending and axial force stresses. The governing equation that was used to calculate the UC Max value is listed at the far right of the spreadsheet in the Eqn column.
The Shear Checkis the maximum ratio of actual to allowable shear stress.
The Loc fields that are to the right of the code check fields tells at what location the maximum code check occurs measured from the I-joint location of the member.
The values (Fc', Ft', Fb, Fv') are the factored allowable stresses per NDS wood member design.
The values (Pr, Tr, Mr, Vr/Wr) are the allowable forces per CSA O86 wood member design. These will only be visible when you have selected the CSA O86-09: Ultimate or CSA O86-14: Ultimate as your wood design code in Model Settings..
Finally, the Equation controlling the
code check is listed. For NDS wood member design, this will be either Eqn. 3.9-1 or 3.9-3. Eqn. 3.9-2 is
not checked since this equation includes the tension stress in a beneficial
(non-conservative) manner. All other requirements in Section 3.9
are also checked, such as fc < FcE1, etc. To see ALL the adjustment
factors and other information used to calculate the factored allowable
stresses, please go to a detail report for the member in question. ![]() .
.
Notes
In some instances code checks are not performed for a particular member. A message explaining why a code check is not possible will be listed instead of the code check value. You may click the cell that contains the message and look to the status bar to view the full message. Following are the messages that may be listed:
This is the general message displayed when code checks were not performed for a member. It could mean that you have not selected a Design Code in Model Settings or you have not included any load combinations for this material type in your solution. Check the Design tab of the Load Combinations spreadsheet.
Section 3.3.3.7 of the NDS code limits the slenderness ratio RB to a maximum of 50. Similarly, clause 7.5.6.4.3 of the CSA O86 limits CB to a maximum of 50. You will need to reduce the effective span length, increase the thickness of the shape, or reduce the depth of the shape.
Section 3.7.1.4 of the NDS code limits the column slenderness ratio of Le1/d or Le2/b to a maximum of 50. You need to reduce your effective length by reducing the actual length between supports or changing the effective length factor “K”. You can also use a thicker shape.
Section 3.9.2 of the NDS code limits the actual axial compressive stress to be less than the term FcE1. This term is approximately the Euler buckling stress for buckling about the strong axis of the member. (Buckling is in the plane of bending)
Section 3.9.2 of the NDS code limits the actual axial compressive stress to be less than the term FcE2. This term is approximately the Euler buckling stress for buckling about the weak axis of the member. (Buckling is in the plane of bending)
Section 3.9.2 of the NDS code limits the actual strong axis bending compressive stress to be less than the term FbE. This term is approximately the lateral buckling stress.