Circular Arc Generation
The circular arc generation lets you generate a full circle or partial arc comprised of beam elements.
Click on image to enlarge it
Circular Arc Generation Options
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Circular Arc - tab |
|
|
Rotation Axis |
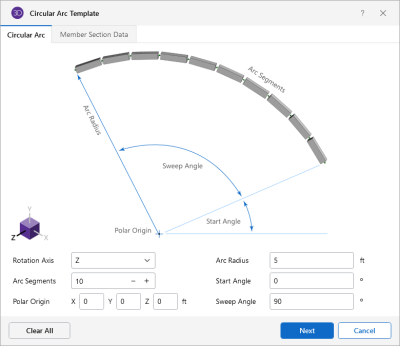
Allows you to define the axis to which the direction of the arc will be oriented. |
|
Arc Segments |
Allows you to define the number or segments the arc is broken into. |
|
Polar Origin |
Allows you to define the reference point from which the arc height and width are measured, and the rotation axis is defined. |
|
Arc Radius |
Allows you to define the distance from the polar origin to the highest point on the parabolic arc. |
|
Start Angle |
Allows you to define the starting angle of the circular arc. |
|
Sweep Angle |
Allows you to define the ending angle of the circular arc. |
|
Member Section Data - tab |
|
|
Material |
Allows you to define the material used to assign the arc member. |
|
Section Set |
Allows you to define the section set assigned for the arc member. |
|
x-x Rotation |
Allows you to define the local x-axis rotation of the arc relative to the global X axis. |
|
Member Prefix |
Allows you to define prefixes to member labels for members created using the circular arc generator. |
|
Node Prefix |
Allows you to define prefixes to node labels for members created using the circular arc generator. |
The polar origin is the center point of the arc. A global axis (X, Y or Z) is entered as the axis of rotation and the arc is in the plane normal to this axis. You can generate an arc the full 360 degrees around the axis of rotation or generate a partial arc by specifying the start and sweep angles.
The arc radius is the length from the polar origin to the arc. The arc increment determines how many piecewise straight segments are used to model the arc.
To generate members for the arc, you
must select a valid section set. This section set is used for
all parts of the arc. If you don’t select a section set, it
generates an arc of joints without members. The “x-axis
rotate” can be used to rotate
the local axes to a desired orientation, however you may find that a
For additional advice on this topic and how to use the Circular Arc to model a Dome structure, please see the RISA Tips & Tricks website: www.risa.com/post/support. Type in Search keywords: 3D Dome.