Grid Generation
This generation enables you to generate
2D or 3D grids
(or even 1D (line) grids) of
Click on image to enlarge it
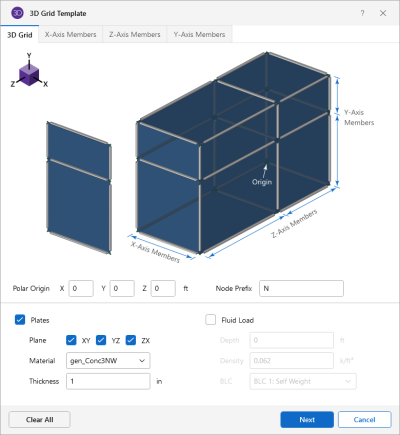
3D Grid Generation Options
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
3D Grid - tab |
|
|
Polar Origin |
Polar Origin defines the reference point from which the arc height and width are measured and the rotation axis is defined. |
|
Node Prefix |
Node Prefix defines prefixes to node labels for members created using the parabolic arc generator. |
|
Plates |
(checkbox) When selected, this option draws plates between members generated using the Grid Generation. |
|
Plane |
Allows you to define which plane the plates are generated for. |
|
Material |
Allows you to define the material used to assign to plate elements. |
|
Thickness |
Allows you to define the thickness of the plate elements. |
|
Fluid Load |
(checkbox) When selected, this option automatically generates hydrostatic loads to the generated plates. |
|
Depth |
Allows you to define the height of which the hydrostatic loads should be applied onto the structure. |
|
Density |
Allows you to define the density of the hydrostatic load that is applied to the structure. |
|
BLC |
Allows you to define the Basic Load Case at which the hydrostatic loads will be generated. |
|
X-Axis Members - tab |
|
|
X-Axis Members |
(checkbox) When selected, this option toggles the members being drawn in the X-Axis. |
|
Material |
Allows you to define the material used to assign the member. |
|
Section Set |
Allows you to define the section set assigned for the member. |
|
x-Axis Rotate |
Allows you to define the local x-axis rotation of the member relative to the global X axis. |
|
Member Prefix |
Allows you to define prefixes to member labels for members created using the Grid generator. |
|
Segments |
(checkbox) When selected, this option allows for the drawing of members into several segments or a single member. |
|
No. of Increments |
Allows you to define how many segments of members to drawn. |
|
Panel Length |
Allows you to define the length of each panel. |
|
Z-Axis Members - tab |
|
|
Z-Axis Members |
(checkbox) When selected, this option toggles the members being drawn in the Z-Axis. |
|
Material |
Allows you to define the material used to assign the member. |
|
Section Set |
Allows you to define the section set assigned for the member. |
|
x-Axis Rotate |
Allows you to define the local x-axis rotation of the member relative to the global X axis. |
|
Member Prefix |
Allows you to define prefixes to member labels for members created using the Grid generator. |
|
Segments |
(checkbox) When selected, this option allows for the drawing of members into several segments or a single member. |
|
No. of Increments |
Allows you to define how many segments of members to drawn. |
|
Panel Length |
Allows you to define the length of each panel. |
|
Y-Axis Members - tab |
|
|
Y-Axis Members |
(checkbox) When selected, this option toggles the members being drawn in the Y-Axis. |
|
Material |
Allows you to define the material used to assign the member. |
|
Section Set |
Allows you to define the section set assigned for the member. |
|
x-Axis Rotate |
Allows you to define the local y-axis rotation of the member relative to the global X axis. |
|
Member Prefix |
Allows you to define prefixes to member labels for members created using the Grid generator. |
|
Segments |
(checkbox) When selected, this option allows for the drawing of members into several segments or a single member. |
|
No. of Increments |
Allows you to define how many segments of members to drawn. |
|
Panel Length |
Allows you to define the length of each panel. |
Define the X,
Y, and Z coordinates of the
You can create members in the global directions between the grid points. You can use different section sets in the three global directions. For example if the Y-axis is the vertical axis you can specify a column shape for the Y-axis members and different or similar beam shapes for the X-axis and Z-axis members.
You can have unique labels assigned to the generated members, by entering a start label. You can also use different labels for the three member directions.
You can create plates in a global plane between the grid points. Keep in mind that the grid increments you define and the global plane(s) you select must be consistent for the plates to be generated. For example, if you defined increments only along the X and Y axes, you’ve defined an XY plane of nodes. If you then enter “ZX” for the plane of the plates, no plates are generated; only the joints in the XY plane would be generated. You would need to specify “XY” as the plane to have the plates generated.
A valid material set must be selected in order for plates to be generated. The default is the first Material listed on the General tab of your Materials spreadsheet.
A hydrostatic load can also be generated along the grid of plates as you generate it. The hydrostatic load is generated using a series of uniform surface loads on your plate elements. If the fluid depth is constant along the grid, you just get uniform loads on your plates. If the fluid depth varies along the grid, you get a series of uniform surface loads that increase in a “stair step” fashion, as you move down the fluid depth. The value of each uniform surface load is equal to the value of the actual hydrostatic load at the mid-point of the plate. The load direction is perpendicular to the plates.
The fluid depth is measured in the positive vertical direction from the starting point for the plate grid.
The default fluid density is for water, but any density can be entered. The Fluid Load BLC provides a drop down list of all the Basic Load Cases. If you’ve defined in any descriptions for your BLC’s, these are shown in the drop down list. The surface loads generated are placed in the selected Basic Load Case.