Parabolic Arc Generation
The Parabolic Arc generation is
used to make arcs that are parabolic. The arc model is comprised
of
Click on image to enlarge it
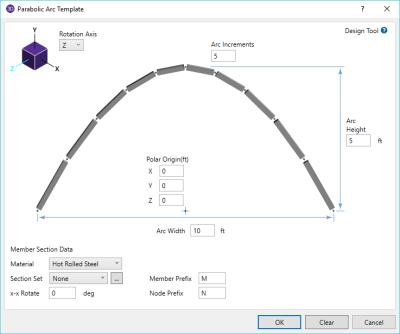
Parabolic Arc Generation Options
|
Option |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Parabolic Arc - tab |
|
|
Rotation Axis |
Allows you to define the axis to which the direction of the arc will be oriented. |
|
Arc Segments |
Allows you to define the number or segments the arc is broken into. |
|
Polar Origin |
Allows you to define the reference point from which the arc height and width are measured and the rotation axis is defined. |
|
Arc Height |
Allows you to define the distance from the polar origin to the highest point on the parabolic arc. |
|
Arc Width |
Allows you to distance between the two ends of the parabolic arc. |
|
Member Section Data - tab |
|
|
Material |
Allows you to define the material used to assign the arc member. |
|
Section Set |
Allows you to define the section set assigned for the arc member. |
|
x-x Rotation |
Allows you to define the local x-axis rotation of the arc relative to the global X axis. |
|
Member Prefix |
Allows you to define prefixes to member labels for members created using the parabolic arc generator. |
|
Node Prefix |
Allows you to define prefixes to node labels for members created using the parabolic arc generator. |
Specify the polar origin about which the arc will be generated.
You must enter the arc height and the arc width and choose a rotation axis.
Enter the number of arc increments to be used to model the arc. The more increments used, the more closely the final geometry follows the desired parabola. The minimum increments are two, which gives you a triangular shape.
You may optionally enter a
To generate members for the arc, you
must select a valid section set. This section set is used for
all parts of the arc. If you don’t select a section set, it generates an arc of