Shape Databases
For each material, there are several databases of common structural shapes such as Hot Rolled Steel, Wood, and Concrete. You may type in the shape names directly, select shapes from these databases or add your own shapes.
What do you want to know?
- What Hot Rolled Steel shapes are available?
- What Concrete shapes are available?
- What Wood shapes are available?
- What are Arbitrary Shapes?
- What are On-Line Shapes?
Database Shape Types
There are different types of shapes for each material type, including
General shapes. Names for each shape type follow a syntax so that
they may be typed directly into the Shape fields in the Beamsand Pile Definitions Spreadsheets. Alternately, you may click the  (ellipsis) button
to open the Shape Selection dialog to assist with selecting or creating shapes.
(ellipsis) button
to open the Shape Selection dialog to assist with selecting or creating shapes.
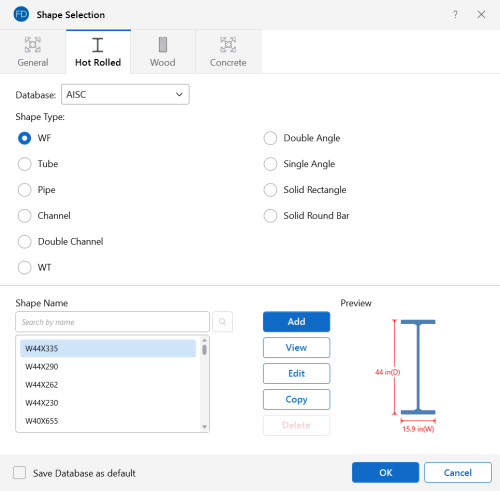
Hot Rolled Shapes
Hot Rolled shapes are accessed
by clicking the Shape Database  button
from the Advanced tab of the ribbon, and then clicking the Hot Rolled tab within the Shape Database Editor dialog.
button
from the Advanced tab of the ribbon, and then clicking the Hot Rolled tab within the Shape Database Editor dialog.
Click on image to enlarge it
Click on image to enlarge it
The hot rolled shapes and databases are more fully described in the Hot Rolled Steel Design section.
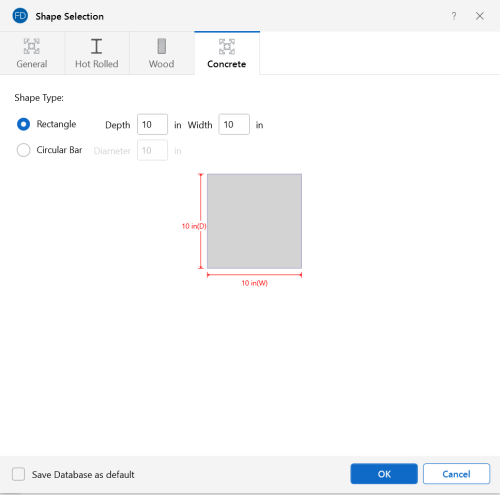
Concrete Shapes
Concrete shapes do not have a predefined database like hot rolled steel and wood. Instead, they are defined using a parametric shape code that may be assigned any depth or width. There are two types of shapes currently supported: Rectangular and Round. For more information, see Beams - Database.
Click on image to enlarge it
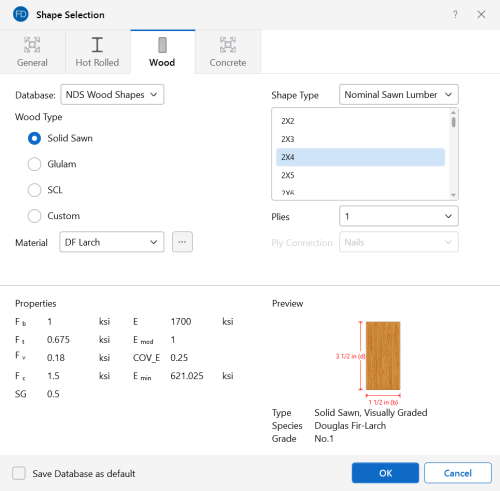
Wood Shapes
The available wood shapes are based on the dimensional lumber and post and timber shapes given in the NDS or CSA O86, depending on which database you have chosen. You may also design for multiple plies of these shapes. Note that the NDS dimensional lumber shapes are all nominal sizes. CSA O86 shapes are actual sizes.
Allowable stress values for each shape are based on the species and grade specified for the selected Material. For more information, see Wood Database.
Click on image to enlarge it
General Shapes
The General Shape type is provided so that additional shapes can be added to the shape database that do not fall within the other available categories.
Code checks are not calculated for general shapes since their place in the relevant specifications is unknown. Everything else will be calculated for them (forces, deflections, stresses).
- Alterations to the Shape Databases are not permanent unless you agree to save them. Changes that are not saved only remain valid for the current session and will not be present the next time you start RISA.
- These shapes will generally be rendered using a greenish cruciform shape. The center of the cruciform will reflect the centroid of the section with the tips of the cruciform representing the distances from the neutral axis to the extreme fiber.
Pipe Database Shapes
Pipe shapes, which are hollow circular shapes, are entered as on-line shapes. The syntax for these shapes is "PIdiaXthick", where "dia" is the pipe outside diameter and "thick" is the pipe thickness (in inches or centimeters). For example (assuming US Standard units), PI10X.5 would be a 10" diameter pipe with a wall thickness of 1/2".
Solid Rectangular Shapes
These shapes can be defined as on-line shapes. The syntax is "REhtXbase", where "ht" is the rectangle height and "base" is the rectangle base (in inches or cm). For example, RE10X4 would be a 10" deep, 4" width rectangular shape (assuming US Standard units). These shapes can also be defined in the Shape Editor. When defined in the Shape Editor, the depth of the solid rectangular section must always be greater than or equal to the width.
Solid Circular Shapes
These shapes are defined as on-line shapes. The syntax is "BARdia", where "dia" is the circle diameter. For example (assuming metric units), BAR2 would be a circular bar with a diameter of 2 cm.
Database Files
The shape databases are stored in the database files (*.FIL). These files may only be edited through the program. The path to these files is set in the File Locations tab of Application Settings, which is found in the File menu.
After adding a new shape in your model, you will be prompted with the Changes to Shape Database dialog, shown below. Click Yes if you want to add the shape to your Shape Database to be available for all future models. Click No if you do not want the new shape to be available for other models, this will not save the shape to your Shape Database.
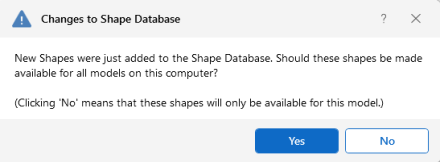
Click on image to enlarge it
You can also make edits to the geometric and section properties of the shapes in your Shape Database. If you modify geometric properties, you can also use the Re-Calc button for the program to automatically calculate the corresponding section properties.
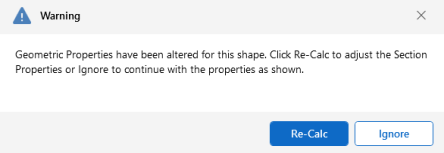
Click on image to enlarge it
- Alterations to the Shape Databases are not permanent unless you agree to save them. Changes that are not saved only remain valid for the current session and will not be present the next time you start RISA.
- New shapes are always added to the bottom of the database in blue text.
- To delete a shape, specify the database and shape type you wish to delete and then click the Delete button.
- To edit a shape, click the Edit button and edit the shape properties. Only shapes that are not part of the default database are able to be edited. If the shape you would like to edit is a default database shape, the program will ask if you would like to make a copy of the shape. Geometric values can be edited here, and will allow you to recalculate the section properties if edits have been made.